The Weekly Anthropocene, March 26 2025
African penguins, resurrection plants, China's grid, German innovations, lion contraceptives, Culdesac Tempe, the Palisades restart, American oystercatchers, and more!
South Africa
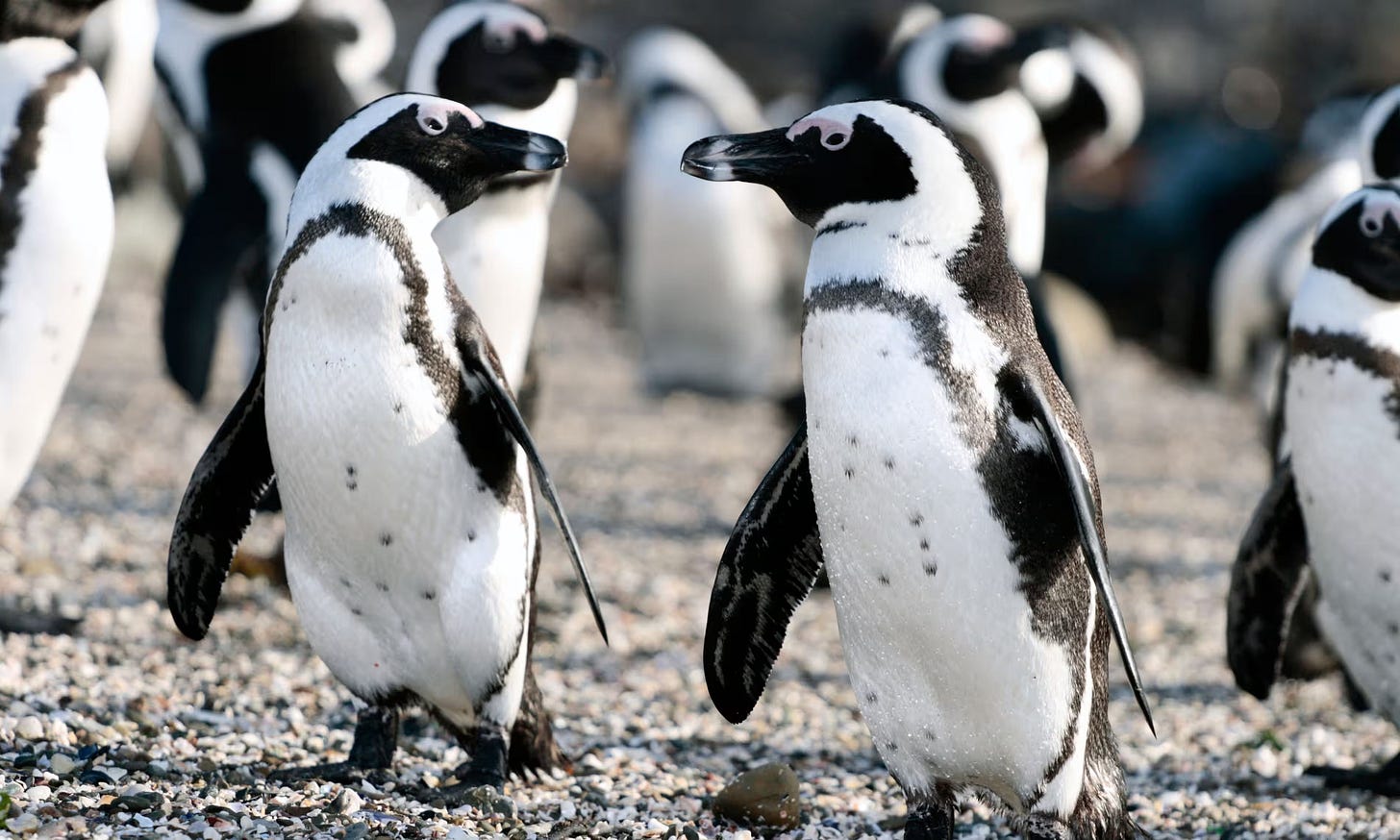

The critically endangered African penguin (Spheniscus demersus) has seen its population plummet by 93% in the last 70 years, with mass overfishing cutting off their food supply. Now, a negotiated legal settlement between fishing industry and conservationist groups, as enforced by a new March 2025 court order, has established no-fishing zones around six key breeding colonies that should last until 2035, creating a potential lifeline for the future of the species. Spectacular work!
The resurrection plants1 of South Africa have evolved extreme desiccation tolerance, with some species able to dry up and survive with zero water for months of drought by vitrifying their own cells and preserving their tissue with protective proteins. Then, if given water, re-green and start photosynthesizing again within days. Now, researchers are studying their biology with the hope of using their genes and/or microbiomes to help give humans’ crops desiccation tolerance in times of water scarcity — potentially an extremely valuable future tool for a warming world!
China
In the first two months of 2025, China reportedly increased spending on its grid by 33% year-on-year to help transport the massive influx of cheap solar power from their ongoing cleantech boom. The nation’s solar capacity grew 43% year-on-year over that same January-February period, with the 39.47 GW of new solar installed accounting for three-quarters of all new power capacity built across China. The major state-owned utilities target spending 820 billion yuan on grid improvements in 2025 to integrate this clean electron bonanza, and new high-voltage power lines are underway. China also nearly quadrupled its battery storage capacity last year, and lots more grid-scale energy storage is in the works. Wow!
China’s fast-growing and world-leading EV industry is reportedly quickly integrating the cutting-edge DeepSeek AI model into the driver experience of its vehicles, joining other uses across the country in smartphones, home appliances, healthcare, and more.
United Kingdom
The Steart Marshes in southwest England have become a model of wetland restoration as a low-cost method of sea level rise adaptation. Previously, flood defenses had kept the sea at bay and turned the area into pastureland, but removing them allowed the rewilding of the original species-rich salt marsh ecosystem — which also helps absorb storm surges and prevent coastal erosion. Great work!
Germany
The legislature of Germany has passed into law a historic trillion-euro spending deal led by new Chancellor Friedrich Merz. Its primary purpose is an industrial, infrastructure, and defense build-up to counter Russian aggression, but the deal also includes 100 million euros earmarked for climate action and clean energy projects plus the addition of a goal to reach climate neutrality (effectively net-zero emissions) by 2045 in the German constitution. The heart of Europe is stepping up! Great news.
The newly unveiled Mercedes CLA sedan looks like German automaking’s most advanced and globally competitive electric vehicle yet, boasting a 792-kilometer battery range2 and able to recharge half that battery in 10 minutes. It starts at an entry-level price of 50,000 euros. This pioneering EV platform is planned to be the blueprint for dozens of future Mercedes models, an encouraging “sign of life” for Germany’s auto sector winning a piece of the future. The Electric Age advances!
A team of German researchers have invented a new method of air conditioning that avoids the need for either burning fossil fuels or using ozone-damaging refrigerant chemicals. The system runs on the cutting-edge “elastocaloric effect” where some masterials have been found to exhibit substantial reversible temperature changes when exposed to mechanical stresses. In the new invention, ultrathin nickel-titanium wires absorb heat when pulled and can controllably release it elsewhere. Elastocaloric cooling looks like a vital fast-emerging new tool for living on a warming planet!
Malawi
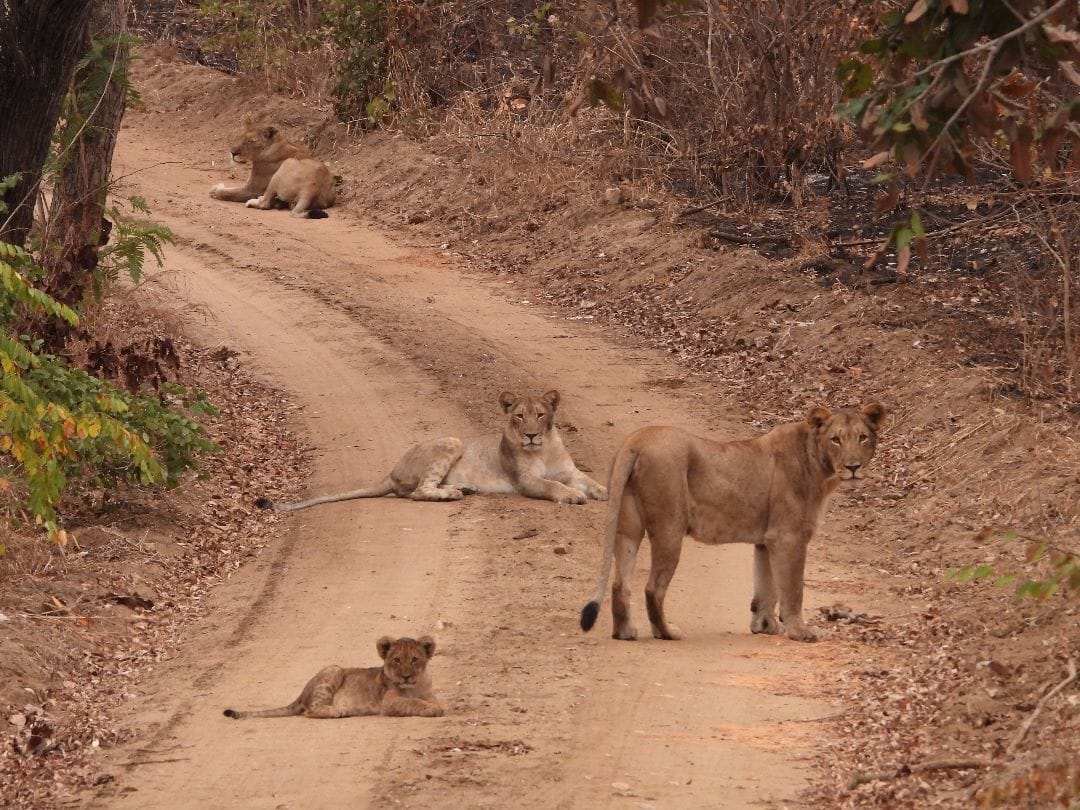
A conservation success in the African nation of Malawi has sparked new innovations in coexistence. In 2012, leading park-management NGO African Parks reintroduced three lions to Malawi’s Majete Wildlife Reserve, and the reserve population has since grown impressively to between 80 and 100 lions. However, this looks close to the maximum the roughly El Paso-sized reserve can support, with 3,000 prey animals killed per year and concerns rising about human-wildlife conflict. So African Parks began a lion contraceptive program in 2022, using hormonal implants for lionesses that humanely reduced cub births from 8-10 yearly to zero in 2024. In the future, they can be removed to allow the lion population to grow again. Fascinating work!
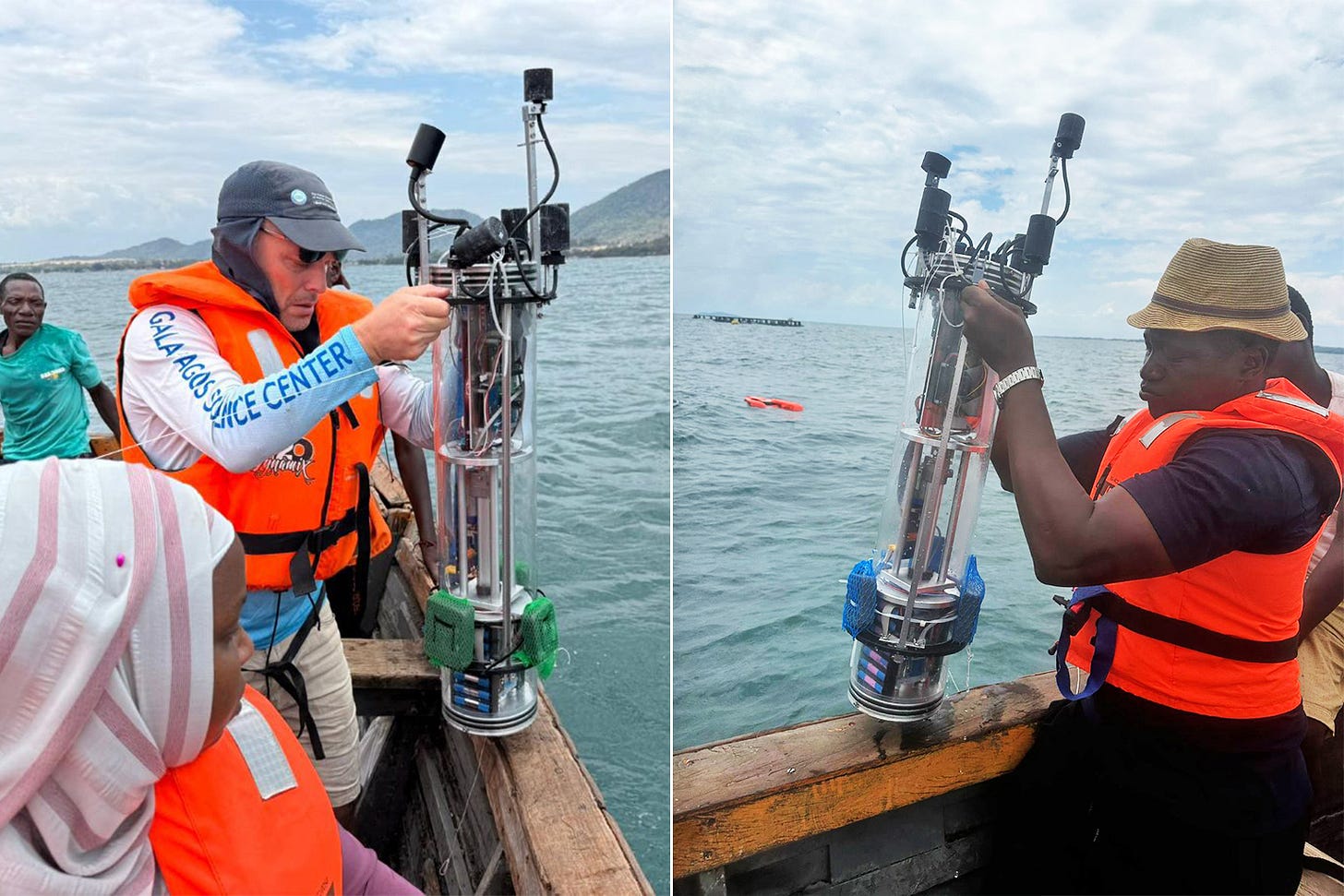
Researchers have tested SOUND, an autonomous solar-powered underwater robot that can locate, count, identify, and track schools of fish, in the waters of Lake Malawi. The hope is that robots like this can improve the efficiency and sustainability of local small-scale fishing by preventing destructive bottom trawling where there are no fish and bycatch of unwanted species. A promising innovation!
Barbados
The Caribbean island nation of Barbados is accelerating its clean energy and climate resilience efforts. Prime Minister Mia Mottley recently hosted a developing countries’ climate action forum, a new plan was announced to reach net-zero emissions by 2035 (up from 15% renewable power now), and funding was just finalized to build a new water reclamation facility boosting resilience to extreme storms. Excellent work!
United States
Though cruel and callous cowards still wreck the executive branch, people across America are still working to build a better Anthropocene and a brighter future.
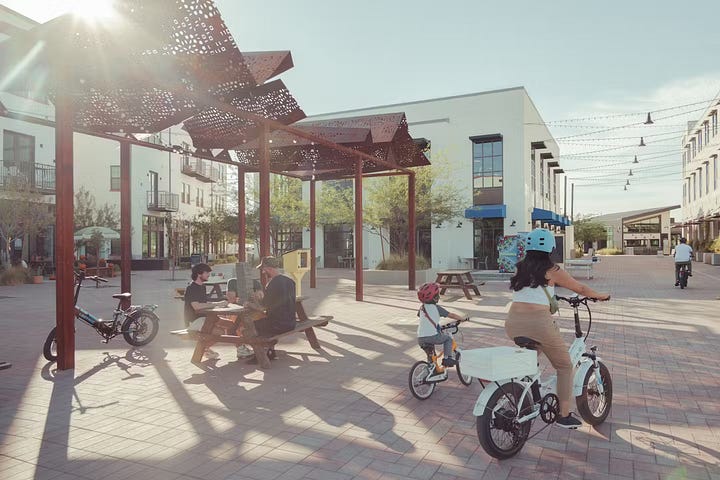
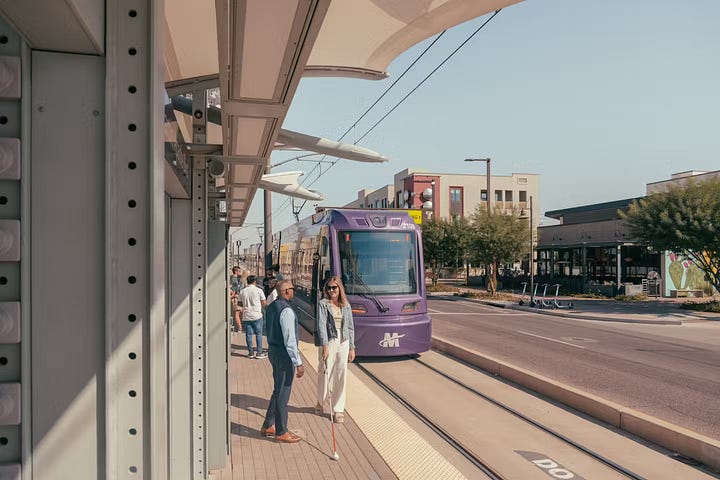


In 2023, a new housing development known as “America’s first car-free neighborhood” opened in Tempe, Arizona. Two years later, Culdesac Tempe is a roaring success, with 300 residents living in 288 apartments with free e-bikes and easy access to a light rail line into the city center. The neighborhood also includes a pool, small retail shops and restaurants, remote workspaces, and a five-dollar-an-hour car rental service for further-flung trips. It’s still being built, with plans to house 1,000 people within three years. A model worth scaling up across America!
The state legislature of Utah has passed America’s first-ever state law in support of plug-in “balcony” solar with unanimous bipartisan support, explicitly exempting the small-scale home solar setups from red tape like interconnection requirements and onerous utility controls and demands. Let’s keep this momentum going!
The New York Times published an excellent interactive map of clean energy worldwide.
Biden Administration advisor Brian Deese has a new essay “Why America Struggles to Build” making an excellent case for why environmentalists should support the emerging Abundance Agenda policy concept. This newsletter is 100% on board!
Startup Boston Metal has successfully produced their first ton of molten steel using a pioneering fossil fuel-free molten oxide electrolysis system! Superb work.
28 U.S. states now get more power from clean energy than from coal.
UtilityDive has a great new article summarizing how grid-scale batteries have made blackouts a thing of the past despite climate stresses across both California and Texas.
U.S. startup Zendure has announced two new home batteries to work with balcony and rooftop solar set-ups. Both use AI for real-time money-saving energy adjustments.
The Department of Energy’s Loan Programs Office, a Green New Deal titan under Biden but hobbled and inactive in recent months, has disbursed a loan to help restart the shuttered 800 MW Palisades nuclear plant in Michigan. The 2024 Palisades restart plan was supported by the Biden Administration and advocated for by this writer. Great to see it happening: we need all the low-carbon electrons we can get!
Mission Solar and its South Korean parent company OCI have announced a new investment of $265 million to build a 2 GW new solar cell manufacturing facility in San Antonio, Texas, using fully supply chain-traced polysilicon from Malaysia. This helps build out the base of the domestic American solar sector; a hopeful sign.
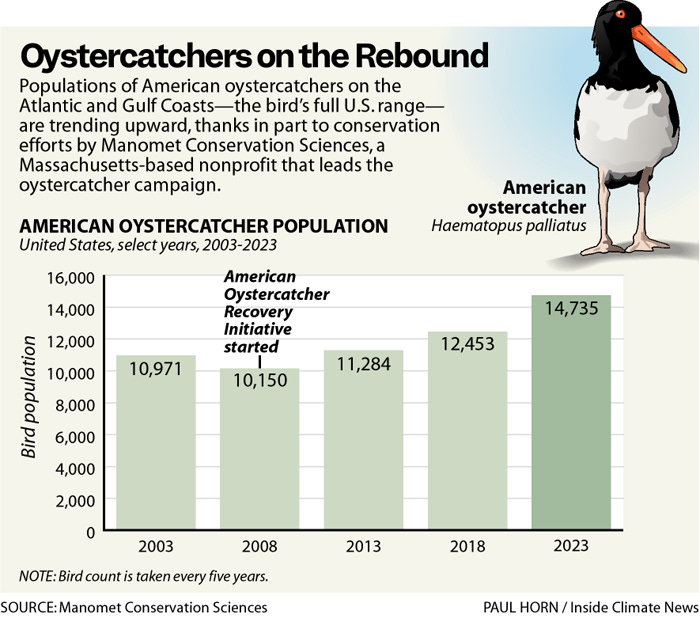
A new report calculates that the American oystercatcher (Haematopus palliatus) population has increased by 45% from 2008 to 2023, reaching an estimated 14,735 birds. Conservation efforts to limit access to key beaches during oystercatcher breeding periods was likely the key intervention — a model for the future. Great work!
This newsletter continues with extra bonus articles for paid subscribers only! Your subscription makes possible more of The Weekly Anthropocene’s data-driven climate & environment progress journalism.
Keep reading with a 7-day free trial
Subscribe to The Weekly Anthropocene to keep reading this post and get 7 days of free access to the full post archives.